Elections are indispensable for delivering democracy. Whether it is incomplete electoral registers, lack of trust in institutions or attempts to rig the system – there are often defects in the quality of elections.
What is electoral integrity?
There are a variety of competing definitions of electoral integrity, but electoral integrity can be defined as: set of principles to be achieved in elections which empower the everyday citizen and help to realize the ideals of democracy (James and Garnett 2025). These principles include: contestation, participation, deliberation and adjudication.
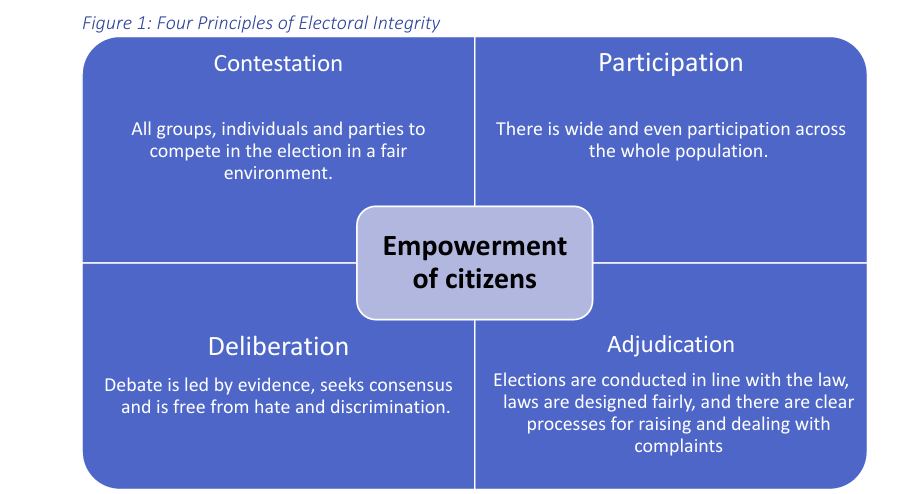
How can electoral integrity be measured?
There are a variety of ways in which the quality of elections can be measured including expert assessments and the views of practitioners.
The advantage of practitioner measures of electoral integrity is that electoral officials have unique practice-based, experiential, tacit knowledge about the conduct of elections, and more insights about the technical aspects of administration of which the public and even experts may be unaware.
Using multiple data sources provides the most reliable and triangulated view.
How does electoral integrity quality around the world?
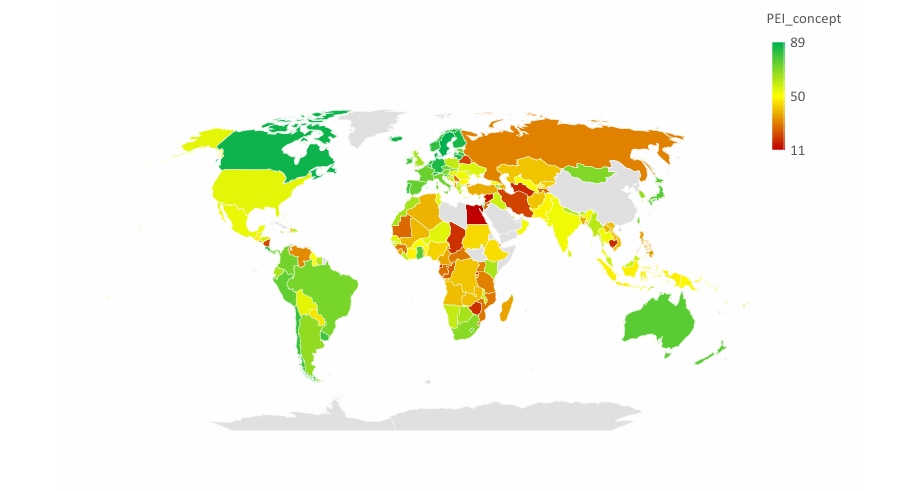
The Electoral Integrity Project’s Annual Global Electoral Integrity Report provides an overview of global patterns of electoral integrity. This is based on the open-source Perceptions of Electoral Integrity Index.
Below is the map of electoral integrity in the 2025 report.
What can improve electoral integrity?
Policy tools can be effective, include:
- Automatic voter registration
- Poll worker recruitment
- Financial investment in electoral management
- International best practice documents
- Not using onous voter identification requirements
- Postal voting with security provisions
- Comparative SWOT against sister countries
- Benchmarking electoral officials’ performance
- Poll worker training
- Building inclusive networks to inform policy making
- Avoiding complex laws
- Electoral risk management approaches
Also see research on specific aspects of electoral integrity:






